Share this:
Posted in:
Efficiency & OptimizationThe beginning process of setting up your storage system
When you get your brand-new storage system delivered and setup into the cloud configuration, you begin the process of meticulously laying out data for optimal usage and performance. At the end of this process you have created a Tetris puzzle of perfection with everything in its proper place. Unfortunately, things are not destined to stay this way. Requirements change, business units and customers change, and new projects enter the environment.
Why is orphaned space important?
Orphaned space is space that is marked as used on the storage system, but is no longer needed by any of the attached hosts. This situation most often occurs when a host system is migrated to new hardware or decommissioned from use. The server is removed, but the notification never makes it to the storage administrator that the space is no longer needed, or the space is purposely kept for a period of time “just in case”.
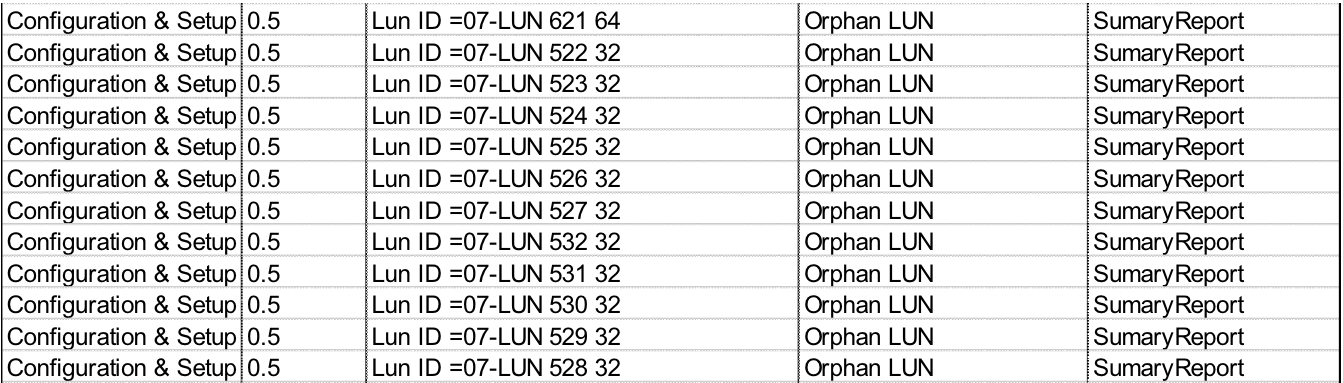
The amount of cloud storage system orphaned space can end up being significant. The use of thin provisioning can make the task of determining orphaned space even more daunting as the size of a lun will not correlate with its used size on disk. With Visual One Intelligence, reports only see the amount of space that is actually used on the cloud storage system as opposed to the allocated space. This is important information if one is quickly attempting to free up space. When servers are removed with luns still existing on the cloud storage system Visual One Intelligence produces a report similar to this:
Archive Data Storage
Archival data storage is data stored on various media types that is stored for a specific period of time for the purpose of data recovery or point in time copies. (E.G. What did the email inbox look like 6 months ago?) This can be stored via a backup software or stored directly on the cloud storage device directly in some cases. The data can be retrieved to restore a corrupted or lost file, or can be used to retrieve data for compliance, lawsuits, audits, or other purposes.
Snapshots – Point in time copies
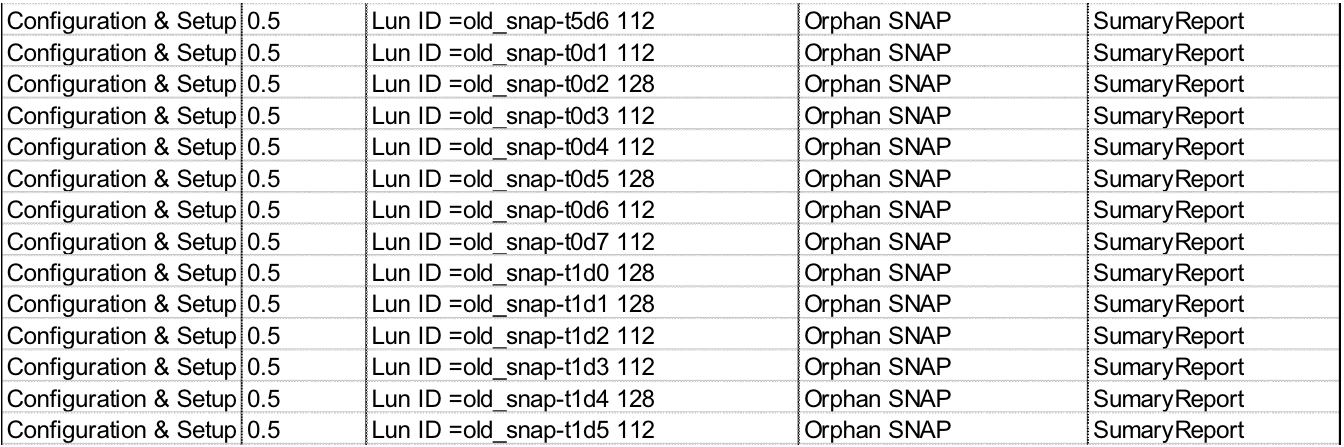
Snapshots are often used on the cloud storage system to help with archival data storage. Snapshots are created and then used to backup data. Snapshots can also be retained for long term archival data storage directly. Just as in the example above these snapshots can outlive their usefulness. Once the process of archival data storage has changed and no longer requires the snapshots, the old snapshots need to be removed to regain the used space. Visual One Intelligence generates a report of snapshots that are no longer associated with the lun from which they were created.
Depending on the Cloud Storage Array type, Manual effort may be required to review the snapshots that are associated with luns to determine if they need to be removed as well. Some models will allow for setting limits on the snapshot retention, based either on the age of the snapshot or the number of snapshots that have been taken. Taking advantage of these options allows for snapshot protection and reduces the likelihood of a snapshot living much past its useful life. The issue of the lun being removed, however, becomes more pronounced. When the underlying lun is deleted, the snapshots may not be and the schedules to clear them out will no longer apply.
Unusable Free Space?
There can be free space available on your cloud storage system, that is not usable. Standard size luns may not have enough space to be created. For example, a standard lun size may be 20GiB and the cloud storage system reports that there is plenty of free space at 85Gib. Upon creation of the lun the administrator finds that there is no pool available on the system with 20 GiB available, despite the overall usable space being within the needed amount. While this is not as simple to fix as removing and orphaned lun or snapshot, Visual One Intelligence provides the lun and pool information required to re-arrange the pools to recapture the hidden free space.
Replication implications
Replication volumes often appear orphaned but should not be counted that way. These luns are created on a remote cloud storage system and the copy of data appears locally. Unless there is an existing DR event it’s unlikely the lun is mapped to a host. This matches the definition of an orphaned lun. Visual One Intelligence analyzes the replication configuration of the cloud storage systems and removes these replicated luns from the orphaned list to avoid customers deleting the needed replicated volumes.
Visual One makes it easier
Visual One Intelligence will find your orphaned space from archival data storage, allowing you to get the fullest use of your cloud storage system. This allows for extended use of devices that are considered full, but can be used further once the orphans are cleaned up. When a cloud storage device reaches end of life and needs replacement clearing (or at least accounting for) orphaned space allows for the purchase of a smaller device than may otherwise appear needed. This is particularly important when the decision is between a traditional spinning disk storage and an all flash solution. The all flash solution often is out of the budget when calculating the “full size” of the cloud storage array. If one finds the “true size” of the array by subtracting orphans one may find that the all flash solution is within the budget.